As the textile industry grapples with its significant carbon footprint, the pursuit of low-carbon energy sources becomes imperative for achieving net-zero emissions. Solar thermal technology, while less prominent compared to other renewable energy sources, offers a promising alternative for decarbonizing industrial heating processes.
Figure: Solar thermal directly heating the water used in the industrial process
Understanding Solar Thermal Technology
Solar thermal technology harnesses sunlight to generate heat, unlike solar photovoltaics (PV) that produce electricity. There are two main categories of solar thermal technologies: non-concentrating and concentrating.
Non-Concentrating Technologies:
- Flat-Plate Collectors (FPC): These collectors absorb sunlight using a dark surface and transfer the heat to a circulating fluid. They are efficient at temperatures up to 100°C.
- Evacuated Tube Collectors (ETC): These consist of glass tubes with heat pipes in a vacuum, significantly reducing heat loss and reaching temperatures up to 120°C.
Concentrating Solar Thermal (CST) Technologies:
- Parabolic Troughs: Use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver tube filled with heat transfer fluid, achieving temperatures up to 400°C.
- Parabolic Dishes: Focus sunlight on a receiver at the dish’s focal point, reaching temperatures up to 1,200°C.
- Power Towers: Employ a field of mirrors to direct sunlight onto a central receiver at the top of a tower, providing high-temperature heat.
- Linear Fresnel Reflectors: Use mirrors to focus sunlight on a fixed receiver, offering varied output temperatures.
Figure: Solar thermal energy used to pre-heat boiler feed water
Advantages of Solar Thermal Energy
- Zero-Emission Heating: One of the most significant advantages of solar thermal technology is its ability to provide zero-emissions heat. This aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
- Economic Viability: The decreasing costs of solar thermal systems, driven by advancements in technology and economies of scale, are enhancing their economic feasibility. Financial incentives and supportive climate policies further improve the attractiveness of solar thermal energy.
- Energy Security: By diversifying energy sources, solar thermal systems can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, mitigating risks associated with fuel price volatility and supply disruptions.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Solar thermal technology is mature and can integrate with existing manufacturing processes. Emerging storage technologies can store excess solar heat for use during non-sunny periods, improving the reliability of solar thermal systems.
Challenges and Barriers
- Suitability for High-Temperature Heat: The textile industry primarily uses steam for heating, which requires temperatures higher than those achievable by most non-concentrating solar thermal systems. Although concentrating solar thermal systems can reach higher temperatures, they are often more complex and costly.
- High Initial Costs: The upfront capital investment for solar thermal systems, including installation and infrastructure modifications, can be substantial. This includes costs for solar collectors, storage systems, and integration with existing heating systems.
- Space Requirements: Solar thermal installations require significant space for collectors and associated infrastructure. This can be a constraint for facilities in urban areas or those with limited available land.
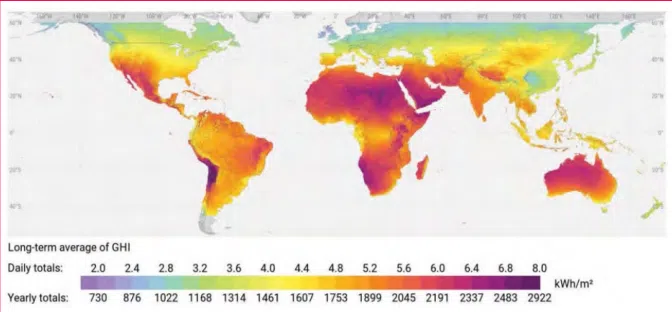
- Geographical Limitations: Solar thermal systems perform best in regions with high and consistent solar irradiation. Countries with lower solar resources or variable sunlight may find it challenging to achieve a consistent heat supply.
- Technical Expertise: The adoption of solar thermal technology may be hindered by a lack of technical expertise and familiarity among stakeholders in the textile industry. There is also competition from more established energy sources and technologies.
Readiness for Adoption
- Availability of Solar Resources: Countries like Egypt, Mexico, Morocco, and Pakistan have high solar resources, making them more suitable for solar thermal technology. In contrast, countries like Germany, Japan, and South Korea have lower solar resources, reducing the viability of solar thermal systems.
- Climate Policy Strength: Countries with strong climate policies and supportive incentives for renewable energy are more likely to adopt solar thermal technology. For instance, Morocco and Spain have robust climate policies that could facilitate the integration of solar thermal systems.
- Technology Supply Chain: The maturity of the solar thermal technology supply chain varies by country. Countries with well-established supply chains, such as those in Europe and North America, are better positioned to implement solar thermal systems.
- Overall Readiness: Composite readiness scores, considering solar resources, climate policy, and technology availability, indicate that countries like China, India, Italy, Morocco, and Spain are among the most prepared to adopt solar thermal technologies. However, challenges such as land constraints and competition with solar PV must be addressed.
Case Studies
While specific examples of solar thermal applications in the textile industry are limited, there are notable successes in other sectors:
- Barrington Brewery & Restaurant, Massachusetts: This facility installed flat-plate solar thermal collectors to provide hot water for brewing and restaurant operations. The system’s success led to an expansion, demonstrating the potential for solar thermal in industrial settings.
- Carlsberg Brewery, Greece: Carlsberg’s Olympic Brewery site uses parabolic trough solar collectors to meet up to 70% of the energy required for can pasteurization during peak sunny months. This installation is expected to reduce CO2 emissions significantly.
Conclusion
Solar thermal technology presents a viable low-carbon energy source for the textile industry, particularly in regions with high solar resources and supportive climate policies. While challenges such as high initial costs, space requirements, and technical expertise must be addressed, the potential benefits of zero-emissions heating and energy security make solar thermal a compelling option. As technology advances and costs decrease, solar thermal could play a crucial role in the textile industry’s transition to net-zero emissions.